Studying the thorax isn’t just another chapter in biology—it’s like learning the blueprint of life’s most essential protection system. And understanding why an organism does or does not have a thorax is where the idea of the apothorax becomes incredibly important.
Let’s break it down in a simple, engaging, and exam-ready way.
Introduction to the Thorax
Meaning of “Thorax”
The thorax is the middle section of the body in many animals, including humans. In humans, it lies between the neck and the abdomen.
Importance of Thoracic Anatomy
It houses the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels—basically the organs that keep you alive every second.
What Happens When the Thorax Is Absent or Reduced
If an organism lacks a thorax—or has a very weak one—it’s known as apothoracic. This can drastically change how that organism functions, moves, and survives.
Understanding the Term “Apothorax”
Definition of Apothorax
Apothorax refers to the absence, reduction, or poor development of the thoracic region.
Origins of the Term
“Apo” means without, and “thorax” means chest region.
Put together, it simply means “without a thorax.”
Why It Matters in Biology
The term helps in:
- Comparative anatomy
- Evolutionary studies
- Understanding segmentation in invertebrates
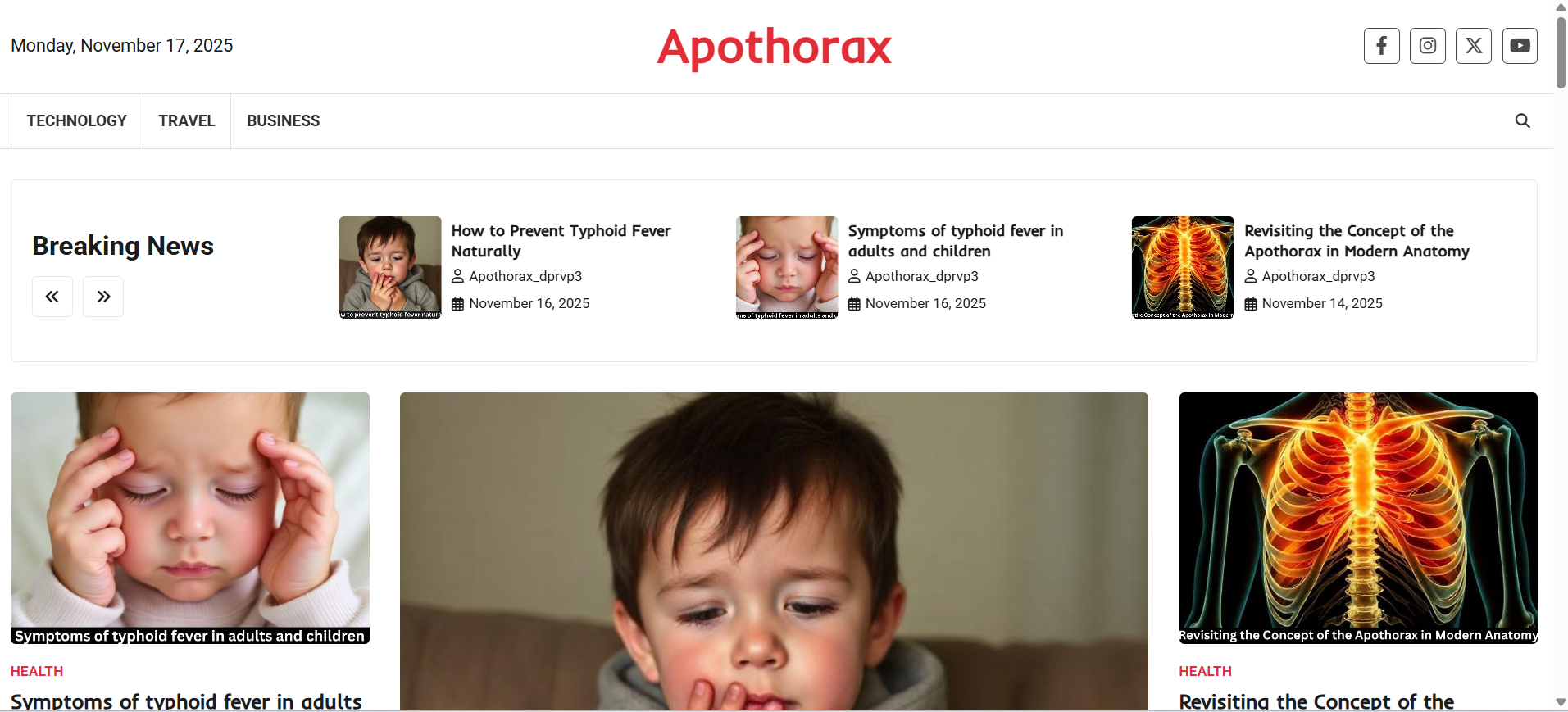
The Human Thorax: Structure and Function
Major Organs Housed in the Thorax
Heart
Pumps oxygen-rich blood throughout the body—your internal engine.
Lungs
Allow gas exchange—oxygen in, carbon dioxide out.
Major Blood Vessels
- Aorta
- Vena cava
- Pulmonary arteries and veins
These are major highways of the circulatory system.
Skeletal Components of the Thorax
The thorax is protected by:
- Ribs
- Sternum
- Thoracic vertebrae
This forms a strong yet flexible cage.
Muscular and Protective Features
- Intercostal muscles
- Diaphragm
These support breathing and protect vital organs.
Why Humans Cannot Have an Apothorax
Evolutionary Significance
Humans evolved with a strong thorax to protect complex internal systems.
Role of the Thorax in Respiration
Breathing depends on:
- Rib movement
- Diaphragm contraction
Without a thorax, oxygenation is impossible.
Why Thoracic Protection Is Essential
Vital organs like the heart and lungs are too delicate to be exposed.
Comparative Anatomy: Apothorax Across Organisms
Animals With a Clear Thorax
Insects, reptiles, birds, mammals—all have a well-defined thorax.
Organisms That Appear Apothoracic
Simple Invertebrates
Worms and some mollusks do not have a defined thorax.
Larval Stages of Arthropods
Caterpillars and maggots show an undivided body, making them functionally apothoracic.
Why Some Species Do Not Need a Thorax
Simple body plans = fewer organs = less need for separation and protection.
Heart, Lungs & Thoracic Protection: A Deep Look
How the Thorax Shields the Heart
The rib cage acts like a helmet, absorbing impact.
Thoracic Cavity and Lung Expansion
The ribs expand and contract, making breathing effortless.
Rib Cage as “Natural Armor”
Injury Prevention
Prevents damage from blows, falls, or pressure.
Pressure Regulation
Maintains internal pressure during respiration.
Apothorax and Survival
How Loss of Thoracic Protection Affects Organisms
Exposure of organs leads to:
- Higher injury risk
- Lower survival rates
- Limited organ complexity
Why Some Small Organisms Survive Without a Thorax
Their organs aren’t as complex or vulnerable.
Size, Complexity & the Need for Protection
Bigger organisms = more complex organs = need for thoracic protection.
Clinical and Educational Importance
Why Students Study Thoracic Anatomy
It helps understand:
- Breathing
- Circulation
- Injury responses
Medical Insight: Link with Trauma & Disease
Thoracic injuries impact life instantly—proof that this structure is irreplaceable.
Understanding Why Thoracic Integrity Saves Lives
From CPR to surgeries, the thorax is central to human survival.
Conclusion
The thorax is more than a body region—it’s your built-in protection system, safeguarding the heart, lungs, and major vessels. Understanding apothorax helps appreciate why the thorax evolved the way it did and why some organisms survive without one. In humans, the absence of a thorax is simply not compatible with life, proving just how essential this region is for respiration, circulation, and protection.
FAQs
1. What is apothorax?
It refers to the absence or underdevelopment of the thoracic region.
2. Can humans be apothoracic?
No. Humans require a thorax for breathing and organ protection.
3. Do insects have a thorax?
Yes. Insects have a well-defined three-part thorax.
4. Which organisms may appear apothoracic?
Simple invertebrates like worms and certain larval forms.
5. Why is the thorax so important?
It protects the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels while enabling breathing.